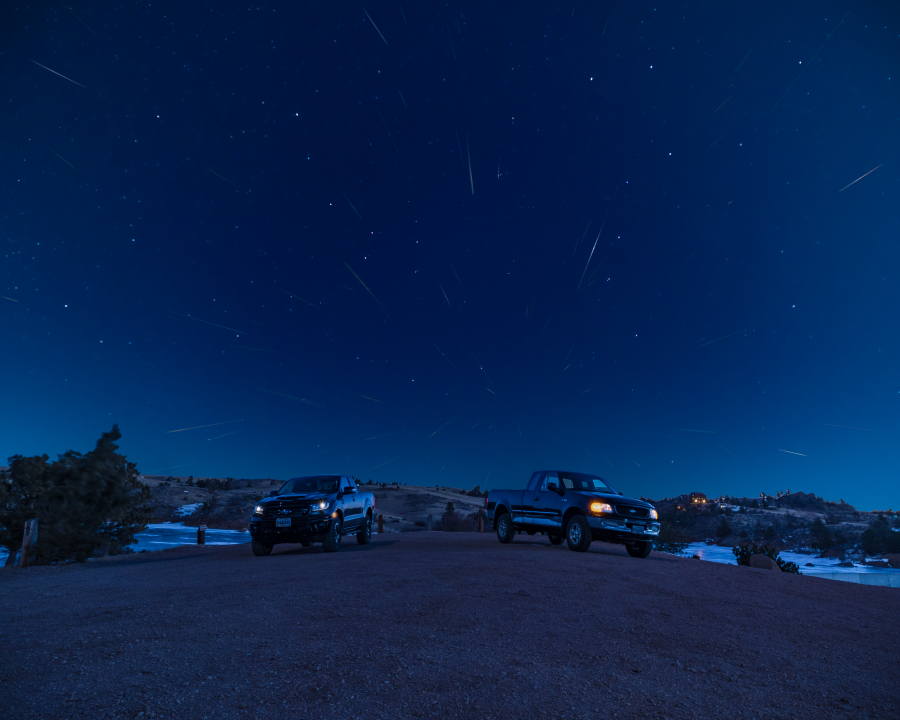

The Quadrantids can be one of the strongest displays of the year, yet they are difficult to observe. The main factor is that the display of strong activity only has a duration of about 6 hours. The reason the peak is so short is due to the shower’s thin stream of particles and the fact that the Earth crosses the stream at a perpendicular angle. Unlike most meteor showers which originate from comets, the Quadrantids have been found to originate from an asteroid. Asteroid 2003 EH1 takes 5.52 years to orbit the sun. It is possible that 2003 EH1 is a “dead comet” or a new kind of object being discussed by astronomers sometimes called a “rock comet.”
These meteors were first noted in 1825 and appeared to radiate from the obsolete constellation of Quadrans Muralis (Mural Quadrant). Today, this area of the sky lies within the boundaries of the constellation of Boötes the herdsman. During early January nights as seen from the northern hemisphere, this area of the sky lies very low in the northwest in the evening sky. Very little activity is normally seen at this time. As the night progresses this area of the sky swings some 40 degrees beneath the northern celestial pole. From areas south of 40 degrees north latitude, it actually passes below the horizon. It then begins a slow rise into the northeastern sky where it obtains a useful altitude around 02:00 local standard time (depending on your latitude). It is between this time and dawn that you will have your best chance to view these meteors. If the peak occurs during this time you will be in for a treat as rates could exceed 100 per hour as seen from rural locations under a moonless sky. Unlike the 2021 shower, when a bright gibbous moon muted the display, the 2022 Quadrantids peak only one day after new moon. This means that the moon will set shortly after sunset and will be invisible at night.
According to the International Meteor Organization’s 2022 Meteor Shower Calendar (page 4) the Quadrantids are predicted to peak near 20:40 Universal Time on January 3, 2021. This timing is most favorable for the Eastern Asian longitudes of the northern hemisphere. High latitude areas of Europe may also witness some activity, even though the radiant will be lower in the evening sky. Those viewing from the southern hemisphere will not see much activity at all as the radiant does not rise very high in their sky before dawn intervenes.
The best strategy to see the most activity is to face the northeast quadrant of the sky and center your view about half-way up in the sky. By facing this direction you be able to see meteors shoot out of the radiant in all directions. This will make it easy to differentiate between the Quadrantids and random meteors from other sources. To provide a scientific useful observing session one needs to carefully note the starting and ending time of your session and the time each meteor appears. The type of meteor needs to be recorded as well as its magnitude. Other parameters that can be recorded are colors, velocity (degrees per second or verbal description) and whether the meteor left a persistent train. Fireballs should be noted and a separate online form filled out after the session.
Serious observers should watch for at least an hour as numerous peaks and valleys of activity will occur. If you only few for a short time it may coincide with a lull of activity. Watching for at least an hour guarantees you will get to see the best this display has to offer. The serious observer is also encouraged to fill out a visual observing form on the website of the International Meteor Organization located. You must register to use the form but this is free.
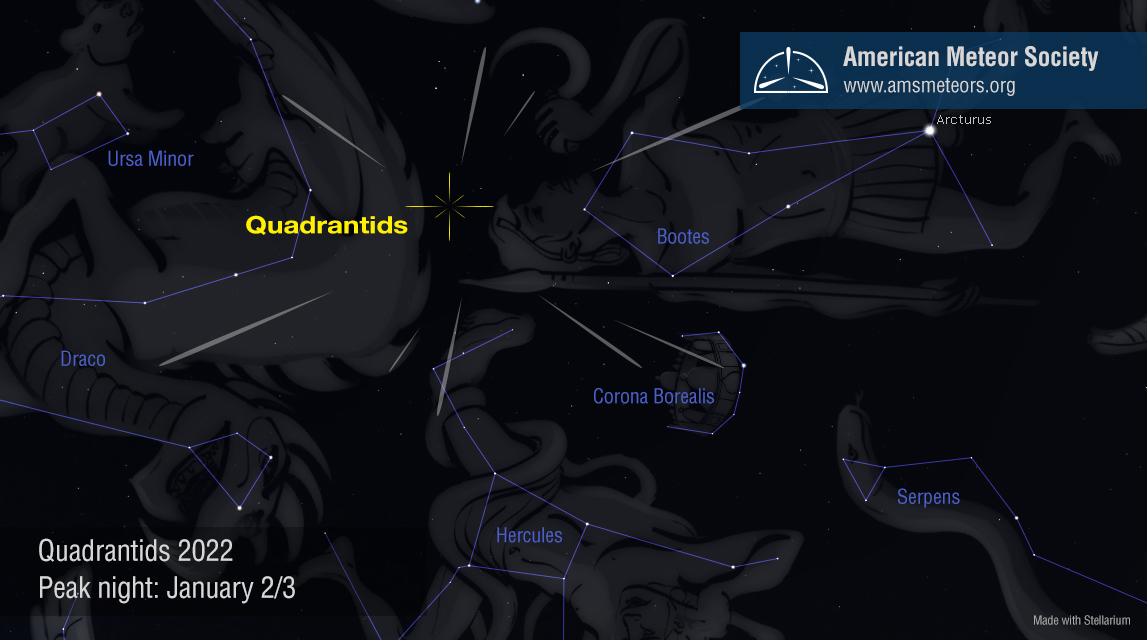
This illustration above depicts the Quadrantid radiant as seen during the morning hours looking low toward the northeast. The brilliant star Arcturus is a good guide to this area of the sky. All Quadrantid meteors will trace back to the radiant area located in northern Bootes. There are several other minor showers active during this time plus random meteors that will appear in different paths than the Quadrantids with different velocities.
The Quadrantids are actually active from 28 December to 12 January, but the mornings away from maximum offer only a small fraction of the activity seen at maximum. In 2023, the Quadrantids are predicted to peak near 03:00 UT on January 4th. This timing favors most of European observers, while the remainder of the world experiences daylight or evening skies when the radiant lies low in the northern skies. Unfortunately the moon will only be two days before full, therefore the bright moon will obscure most of the activity. Therefore we hope you will take advantage of the dark conditions present for the 2022 display. We look forward to seeing your results of this year’s display!




 You saw something bright and fast? Like a huge shooting star? Report it: it may be a fireball.
You saw something bright and fast? Like a huge shooting star? Report it: it may be a fireball.  You counted meteors last night? Share your results with us!
You counted meteors last night? Share your results with us!  You took a photo of a meteor or fireball? You have a screenshot of your cam? Share it with us!
You took a photo of a meteor or fireball? You have a screenshot of your cam? Share it with us!  You caught a meteor or fireball on video? Share your video with us!
You caught a meteor or fireball on video? Share your video with us!
3 comments
This could be very interesting from an amateur radio or radio meteor hunter perspective due to the direction & intensity. While we in N.America will miss the most (especially here in SW USA @ 33N -112W) perhaps good scatter can still be obtained after day break, providing returns & even 2-way deep inside the polar region.
I’m most surprised that I don’t remember hearing of this shower before. I came here from SpaceWeather.com which linked here. Learn something every day!
I have been doing meteor scatter with my DTV antenna for about two years now and it works well, especially for this shower peak during the day is South Carolina. I have been detecting about 5 per minute so far this morning so the peak later today should be good!
Hey hi SW USA! I’m in Northern Arizona if ur close try to get in contact I’d love to join ur group.
I saw a massive one maybe it was 2 last nite around 10:15pm it was the biggest hugest one ive ever seen!