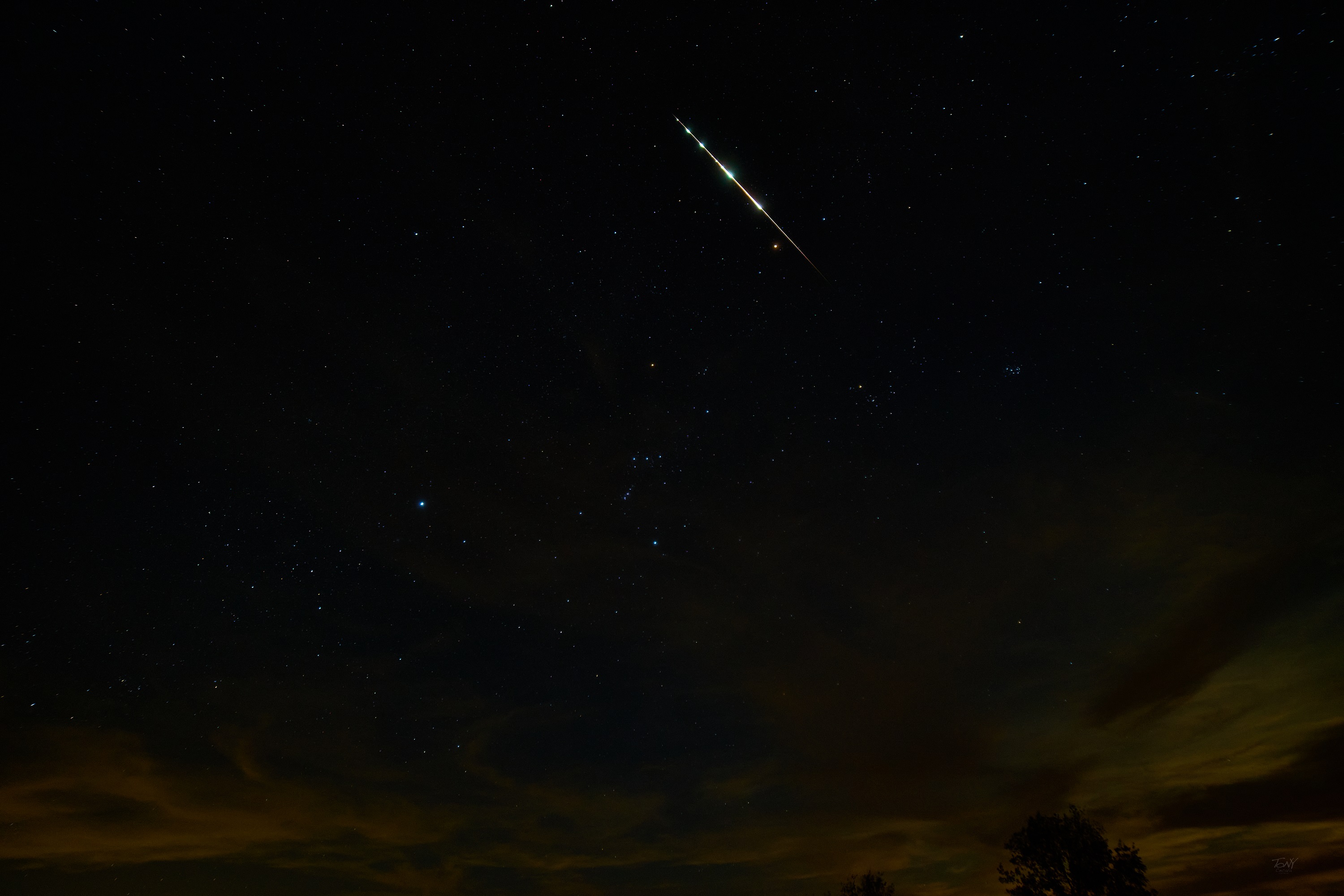
 Dr. Tony Cecala captured this bright multi-bursting Taurid fireball on November 6, 2022, at 05:51 CST (10:51 UT) from Lone Grove, Oklahoma, USA. © Dr. Tony Cecala (tonycecala.com)
Dr. Tony Cecala captured this bright multi-bursting Taurid fireball on November 6, 2022, at 05:51 CST (10:51 UT) from Lone Grove, Oklahoma, USA. © Dr. Tony Cecala (tonycecala.com)Meteor activity kicks into high gear in August as seen from the northern hemisphere. The main reason for all this activity is the Perseid shower that peak on August 13th. This shower is active most of the month and remains above the level of the sporadic background for a week centered on August 13th. The sporadic activity is also near maximum as seen from the northern hemisphere and is now more than double the rates from just three months ago. As seen from the southern hemisphere, meteor rates are still decent but falling rapidly. The sporadic rates continue their downward slide plus the Perseid radiant does not rise high into the sky as seen in the southern hemisphere. Therefore, rates for the Perseids are greatly reduced when compared to those seen from the northern hemisphere.
During this period, the moon reaches its full phase on Tuesday August 1st. During this entire period the moon will lie above the horizon most of the night making it difficult to observe meteor activity. The estimated total hourly rates for evening observers this week should be near 3 as seen from mid-northern latitudes (45N) and 3 as seen from tropical southern locations (25S) For morning observers, the estimated total hourly rates should be near 18 as seen from mid-northern latitudes (45N) and 16 as seen from tropical southern locations (25S). Rates are reduced due to interfering moonlight. The actual rates seen will also depend on factors such as personal light and motion perception, local weather conditions, alertness, and experience in watching meteor activity. Note that the hourly rates listed below are estimates as viewed from dark sky sites away from urban light sources. Observers viewing from urban areas will see less activity as only the brighter meteors will be visible from such locations.
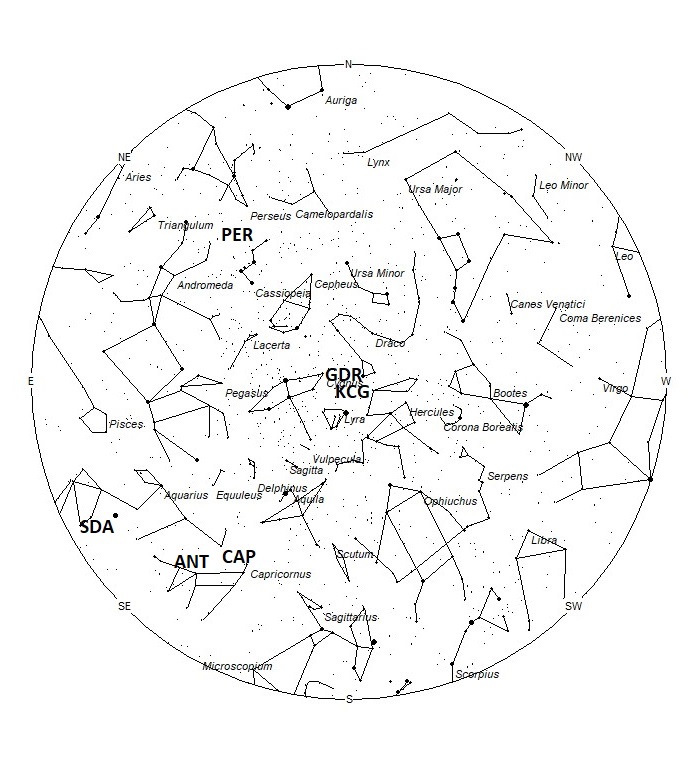
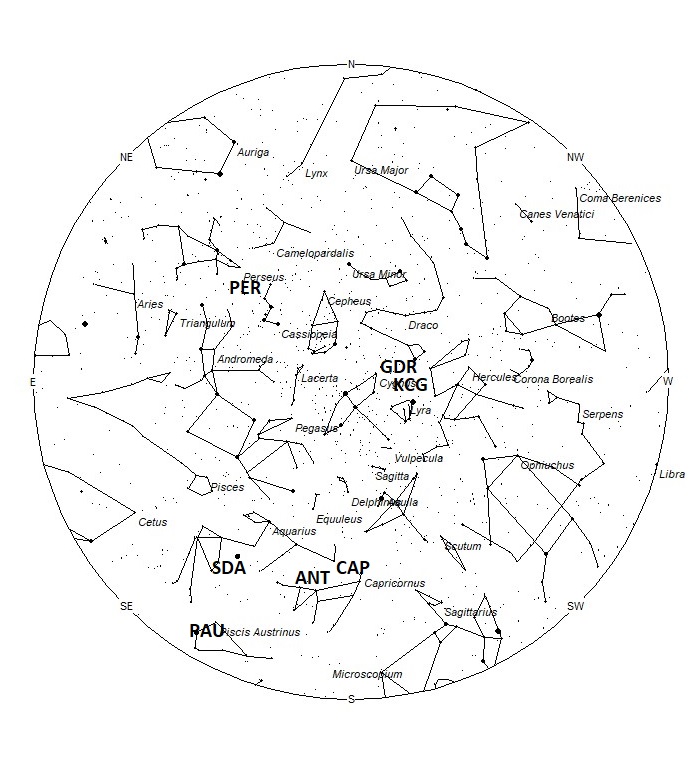
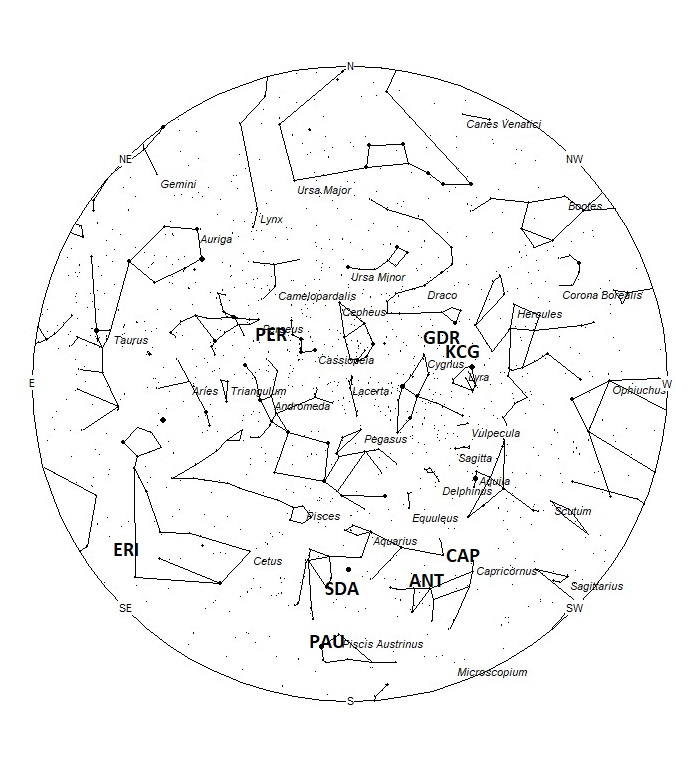
The radiant (the area of the sky where meteors appear to shoot from) positions and rates listed below are exact for Saturday night/Sunday morning July 29/30. These positions do not change greatly day to day so the listed coordinates may be used during this entire period. Most star atlases (available at science stores and planetariums) will provide maps with grid lines of the celestial coordinates so that you may find out exactly where these positions are located in the sky. I have also included charts of the sky that display the radiant positions for evening, midnight, and morning. The center of each chart is the sky directly overhead at the appropriate hour. These charts are oriented for facing south but can be used for any direction by rotating the charts to the desired direction. A planisphere or computer planetarium program is also useful in showing the sky at any time of night on any date of the year. Activity from each radiant is best seen when it is positioned highest in the sky, either due north or south along the meridian, depending on your latitude. Radiants that rise after midnight will not reach their highest point in the sky until daylight. For these radiants, it is best to view them during the last few hours before dawn. It must be remembered that meteor activity is rarely seen at its radiant position. Rather they shoot outwards from the radiant, so it is best to center your field of view so that the radiant lies toward the edge and not the center. Viewing there will allow you to easily trace the path of each meteor back to the radiant (if it is a shower member) or in another direction if it is sporadic. Meteor activity is not seen from radiants that are located far below the horizon. The positions below are listed in a west to east manner in order of right ascension (celestial longitude). The positions listed first are located further west therefore are accessible earlier in the night while those listed further down the list rise later in the night.
These sources of meteoric activity are expected to be active this week.
Details of each source will continue next week when viewing conditions are more favorable.
The list below offers the information in tabular form. Rates and positions are exact for Saturday night/Sunday morning except where noted in the shower descriptions.
| SHOWER | DATE OF MAXIMUM ACTIVITY |
CELESTIAL POSITION | ENTRY VELOCITY | CULMINATION | HOURLY RATE | CLASS |
| RA (RA in Deg.) DEC | Km/Sec | Local Summer Time | North-South | |||
| kappa Cygnids (KCG) | Aug 17 | 18:32 (278) +41 | 23 | 23:00 | <1 – <1 | IV |
| July gamma Draconids (GDR) | Jul 28 | 18:39 (280) +51 | 27 | 23:00 | <1 – <1 | II |
| alpha Capricornids (CAP) | Jul 30 | 20:28 (307) -10 | 23 | 01:00 | 3 – 3 | II |
| Anthelion (ANT) | – | 21:16 (319) -15 | 30 | 02:00 | 1 – 2 | II |
| Southern delta Aquariids (SDA) | Jul 30 | 22:40 (340) -16 | 41 | 03:00 | 3 – 5 | I |
| Piscis Austrinids (PAU) | Jul 28 | 22:52 (343) -29 | 35 | 03:00 | <1 – 1 | II |
| Perseids (PER) | Aug 13 | 01:56 (029) +54 | 59 | 07:00 | 5 – 2 | I |
| eta Eridanids (ERI) | Aug 08 | 02:16 (034) -16 | 64 | 07:00 | <1 – <1 | II |
Class Explanation: A scale to group meteor showers by their intensity:
- Class I: the strongest annual showers with Zenith Hourly Rates normally ten or better.
- Class II: reliable minor showers with ZHR’s normally two to ten.
- Class III: showers that do not provide annual activity. These showers are rarely active yet have the potential to produce a major display on occasion.
- Class IV: weak minor showers with ZHR’s rarely exceeding two. The study of these showers is best left to experienced observers who use plotting and angular velocity estimates to determine shower association. These weak showers are also good targets for video and photographic work. Observers with less experience are urged to limit their shower associations to showers with a rating of I to III.




 You saw something bright and fast? Like a huge shooting star? Report it: it may be a fireball.
You saw something bright and fast? Like a huge shooting star? Report it: it may be a fireball.  You counted meteors last night? Share your results with us!
You counted meteors last night? Share your results with us!  You took a photo of a meteor or fireball? You have a screenshot of your cam? Share it with us!
You took a photo of a meteor or fireball? You have a screenshot of your cam? Share it with us!  You caught a meteor or fireball on video? Share your video with us!
You caught a meteor or fireball on video? Share your video with us!