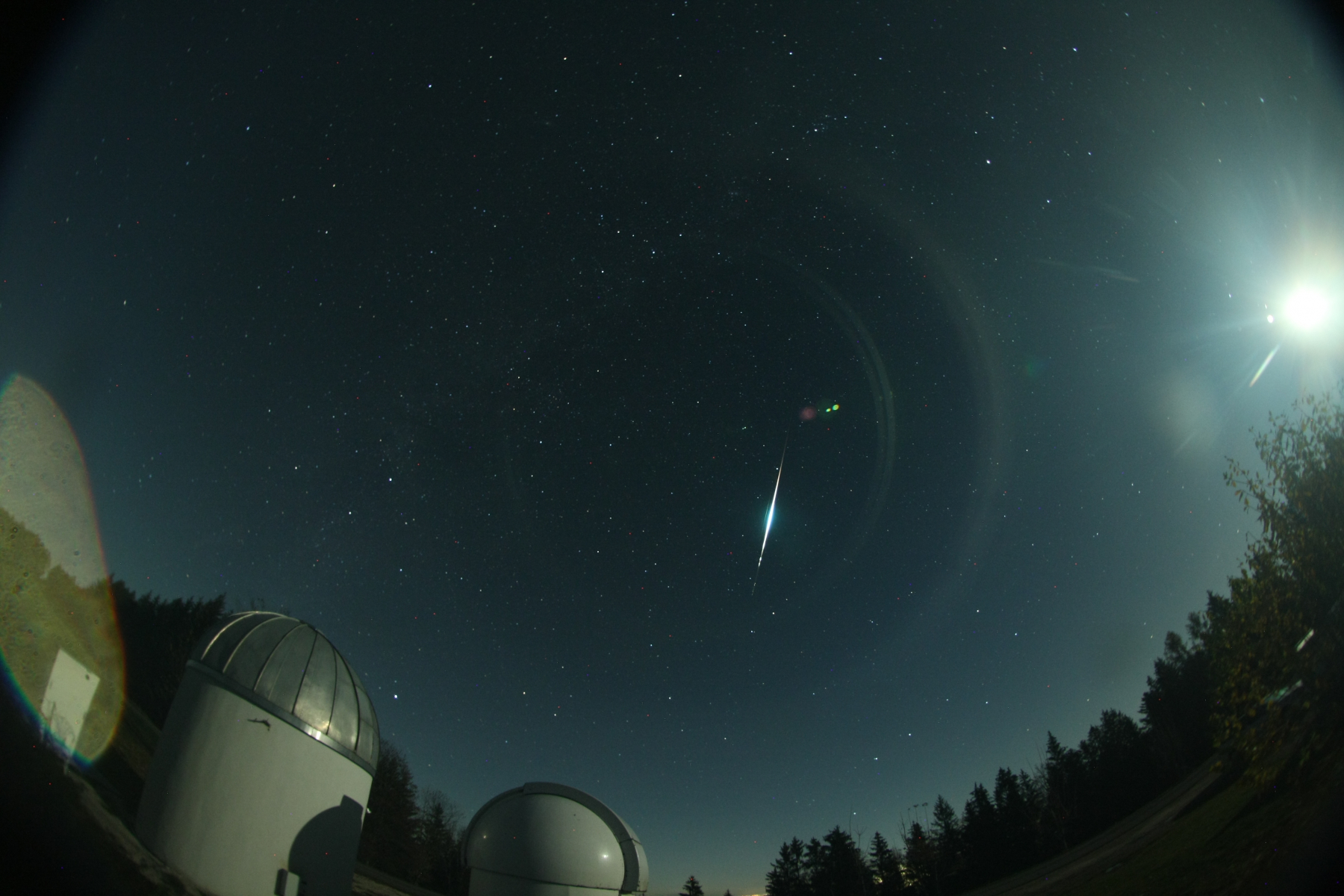
 Erwin Filimon’s automated camera picked up this impressive fireball at 21:56 UT on 6 November 2020, from Weyregg am Attersee, Austria. For more on this fireball visit: https://fireball.amsmeteors.org/members/imo_view/event/2020/6365 Credit Erwin Filimon
Erwin Filimon’s automated camera picked up this impressive fireball at 21:56 UT on 6 November 2020, from Weyregg am Attersee, Austria. For more on this fireball visit: https://fireball.amsmeteors.org/members/imo_view/event/2020/6365 Credit Erwin FilimonDuring this period, the moon reaches its full phase on Friday January 29th. At this time, the moon is located opposite the sun, thus it will rise as the sun sets and set as the sun rises. This weekend the waxing gibbous moon will set during the early morning hours, leaving a small period of time free from interfering moonlight. The estimated total hourly meteor rates for evening observers this week is near 2 as seen from mid-northern latitudes and 3 as seen from tropical southern locations (25S). For morning observers, the estimated total hourly rates should be near 12 as seen from mid-northern latitudes (45N) and 12 as seen from tropical southern locations (25S). The actual rates will also depend on factors such as personal light and motion perception, local weather conditions, alertness, and experience in watching meteor activity. Evening rates are reduced during this period due to moonlight. Note that the hourly rates listed below are estimates as viewed from dark sky sites away from urban light sources. Observers viewing from urban areas will see less activity as only the brighter meteors will be visible from such locations.
The radiant (the area of the sky where meteors appear to shoot from) positions and rates listed below are exact for Saturday night/Sunday morning January 23/24. These positions do not change greatly day to day so the listed coordinates may be used during this entire period. Most star atlases (available at science stores and planetariums) will provide maps with grid lines of the celestial coordinates so that you may find out exactly where these positions are located in the sky. A planisphere or computer planetarium program is also useful in showing the sky at any time of night on any date of the year. Activity from each radiant is best seen when it is positioned highest in the sky, either due north or south along the meridian, depending on your latitude. It must be remembered that meteor activity is rarely seen at the radiant position. Rather they shoot outwards from the radiant, so it is best to center your field of view so that the radiant lies at the edge and not the center. Viewing there will allow you to easily trace the path of each meteor back to the radiant (if it is a shower member) or in another direction if it is sporadic. Meteor activity is not seen from radiants that are located far below the horizon. The positions below are listed in a west to east manner in order of right ascension (celestial longitude). The positions listed first are located further west therefore are accessible earlier in the night while those listed further down the list rise later in the night.
These sources of meteoric activity are expected to be active this week.
.
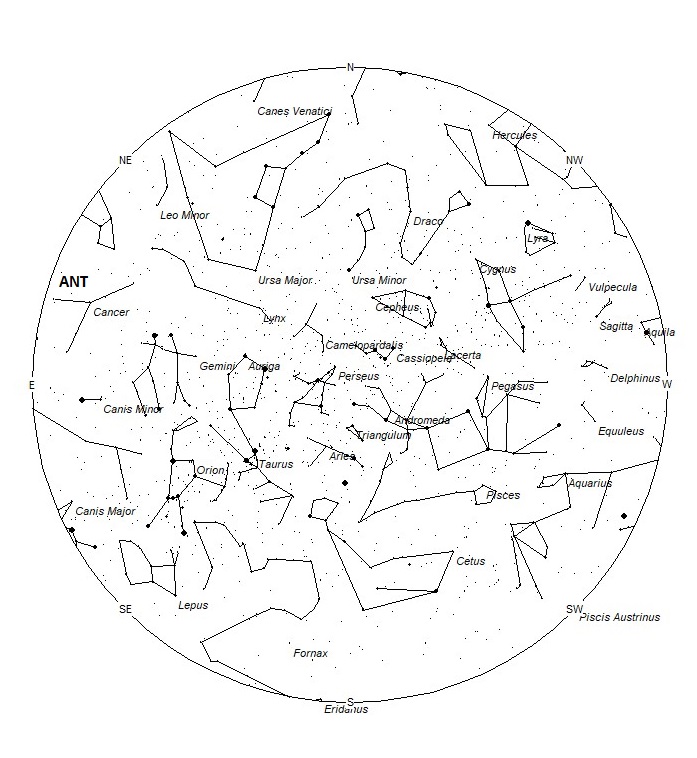
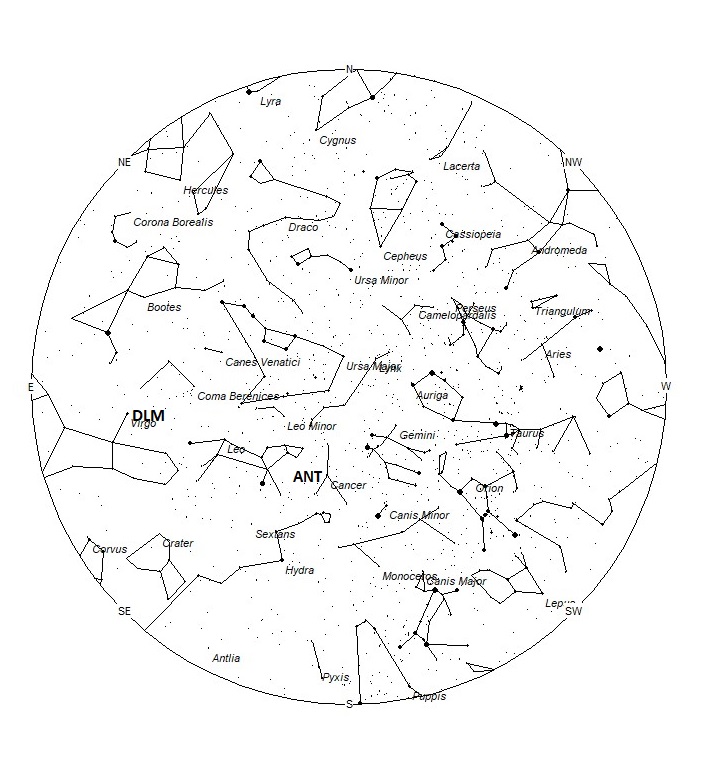
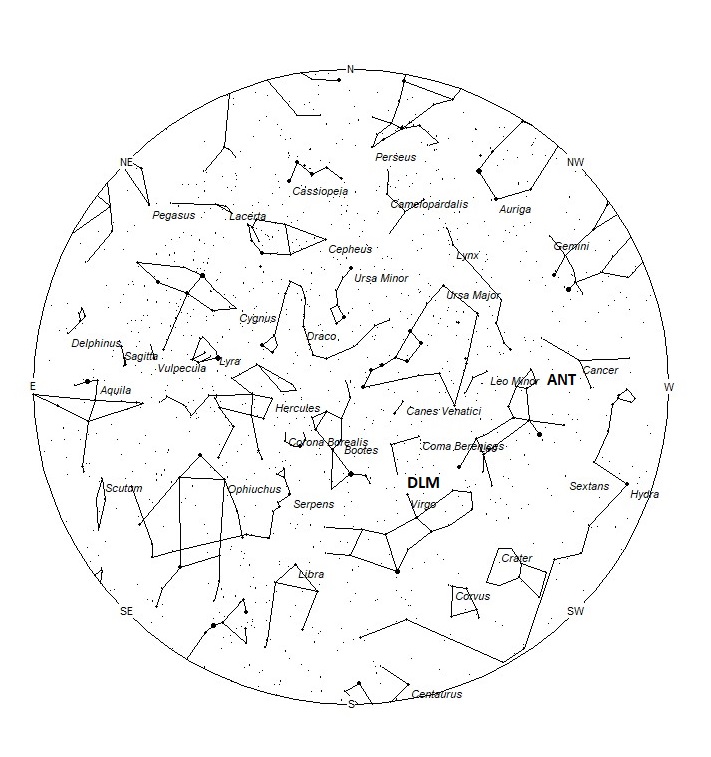
The Anthelion (ANT) radiant is active from a position located at 09:08 (137) +16. This position lies in eastern Cancer, 5 degrees southeast of the 4th magnitude star known as Asellus Australis (delta Cancri). This radiant is a very large oval some thirty degrees wide by fifteen degrees high. Activity from this radiant can appear from more than one constellation., This week these meteors can also be seen from western Leo and well as Cancer. There are several lists that have the delta Cancrids currently active, but we include them with the Anthelions as the celestial positions overlap. The position listed here is for the center of the radiant. This radiant is best placed near 01:00 Local Standard Time (LST) when it lies on the meridian and is highest in the sky. Rates at this time should be near 2 per hour as seen from the northern hemisphere and 1 per hour as seen from south of the equator. With an entry velocity of 30 km/sec., the average Anthelion meteor would be of slow velocity.
The December Leonis Minorids (DLM) are a shower of long duration active from November 22 through February 10th. Maximum occurred near December 20th. The radiant is currently located at 12:48 (192) +14. This position lies in southern Coma Berenices, 4 degrees northwest of the 3rd magnitude star known as Vindemiatrix (epsilon Virginis). These meteors are best seen near 0500 LST when the radiant lies highest above the horizon. Current hourly rates are expected to be near less than 1 no matter your location. At 63 km/sec. the December Leonis Minorids produce mostly swift meteors.
As seen from the mid-northern hemisphere (45N) one would expect to see approximately 8 sporadic meteors per hour during the last hour before dawn as seen from rural observing sites. Evening rates would be near 1 per hour. As seen from the tropical southern latitudes (25S), morning rates would be near 11 per hour as seen from rural observing sites and 2 per hour during the evening hours. Locations between these two extremes would see activity between the listed figures. Evening rates are reduced due to moonlight.
The list below offers the information from above in tabular form. Rates and positions are exact for Saturday night/Sunday morning except where noted in the shower descriptions.
| SHOWER | DATE OF MAXIMUM ACTIVITY | CELESTIAL POSITION | ENTRY VELOCITY | CULMINATION | HOURLY RATE | CLASS |
| RA (RA in Deg.) DEC | Km/Sec | Local Standard Time | North-South | |||
| Anthelion (ANT) | – | 09:08 (137) +16 | 30 | 01:00 | 2 – 1 | II |
| December Leonis Minorids (DLM) | Dec 20 | 12:48 (192) +14 | 63 | 05:00 | <1 – <1 | II |



 You saw something bright and fast? Like a huge shooting star? Report it: it may be a fireball.
You saw something bright and fast? Like a huge shooting star? Report it: it may be a fireball.  You counted meteors last night? Share your results with us!
You counted meteors last night? Share your results with us!  You took a photo of a meteor or fireball? You have a screenshot of your cam? Share it with us!
You took a photo of a meteor or fireball? You have a screenshot of your cam? Share it with us!  You caught a meteor or fireball on video? Share your video with us!
You caught a meteor or fireball on video? Share your video with us!